Rectifier,Half wave rectifiers,Half Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter, Full Wave Rectifier,Graetz bridge rectifier: a full-wave rectifier using four diodes, Full-wave rectifier using a center tap transformer and 2 diodes, full Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter,Diode bridge,Bridge Rectifier, full wave bridge rectifier circuit, full wave bridge rectifier circuit with capacitor filter
Rectifier
KBPC2504 Bridge Rectifier Diode
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, includingvacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, copper and selenium oxide rectifiers, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motors have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a "cat's whisker" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or "crystal detector".
Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems. Rectification may serve in roles other than to generate direct current for use as a source of power. As noted,detectors of radio signals serve as rectifiers. In gas heating systems flame rectification is used to detect presence of a flame.
Because of the alternating nature of the input AC sine wave, the process of rectification alone produces a DC current that, though unidirectional, consists of pulses of current. Many applications of rectifiers, such as power supplies for radio, television and computer equipment, require a steady constant DC current (as would be produced by a battery). In these applications the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic filter (usually a capacitor) to produce a steady current.
KBPC2504 Bridge Rectifier Diode
Half wave rectifiers
In half-wave rectification of a single-phase supply, either the positive or negative half of the AC wave is passed, while the other half is blocked. Because only one half of the input waveform reaches the output, mean voltage is lower. Half-wave rectification requires a single diode in a single-phase supply, or three in a three-phase supply. Rectifiers yield a unidirectional but pulsating direct current; half-wave rectifiers produce far more ripple than full-wave rectifiers, and much more filtering is needed to eliminate harmonics of the AC frequency from the output.
The no-load output DC voltage of an ideal half-wave rectifier for a sinusoidal input voltage is:
where:
- Vdc, Vav – the DC or average output voltage,
- Vpeak, the peak value of the phase input voltages,
- Vrms, the root-mean-square value of output voltage.
Half Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter
- A full-wave rectifier converts the whole of the input waveform to one of constant polarity (positive or negative) at its output. Full-wave rectification converts both polarities of the input waveform to pulsating DC (direct current), and yields a higher average output voltage. Two diodes and a center tapped transformer, or four diodes in a bridge configurationand any AC source (including a transformer without center tap), are needed.Single semiconductor diodes, double diodes with common cathode or common anode, and four-diode bridges, are manufactured as single components.
- For single-phase AC, if the transformer is center-tapped, then two diodes back-to-back (cathode-to-cathode or anode-to-anode, depending upon output polarity required) can form a full-wave rectifier. Twice as many turns are required on the transformer secondary to obtain the same output voltage than for a bridge rectifier, but the power rating is unchanged.
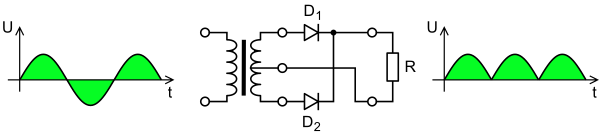
Full-wave rectifier using a center tap transformer and 2 diodes.- Very common double-diode rectifier vacuum tubes contained a single common cathode and two anodes inside a single envelope, achieving full-wave rectification with positive output. The 5U4 and 5Y3 were popular examples of this configuration.
full Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter
- Diode bridge
- A diode bridge is an arrangement of four (or more) diodes in a bridge circuit configuration that provides the same polarity of output for either polarity of input.When used in its most common application, for conversion of an alternating current (AC) input into a direct current (DC) output, it is known as a bridge rectifier. A bridge rectifier provides full-wave rectification from a two-wire AC input, resulting in lower cost and weight as compared to a rectifier with a 3-wire input from a transformer with a center-tapped secondary winding.The essential feature of a diode bridge is that the polarity of the output is the same regardless of the polarity at the input.
Bridge Rectifier
- A bridge rectifier is an arrangement of four or more diodes in a bridge circuit configuration which provides the same output polarity for either input polarity. It is used for converting an alternating current (AC) input into a direct current (DC) output. A bridge rectifier provides full-wave rectification from a two-wire AC input, therefore resulting in lower weight and cost when compared to a rectifier with a 3-wire input from a transformer with a center-tapped secondary winding.
- full wave bridge rectifier circuit
- full wave bridge rectifier circuit with capacitor filter
-
trending keywords on this topic / related keywords / trending hashtags- Rectifier
- Half wave rectifiers
Half Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter
Full Wave Rectifier
Graetz bridge rectifier: a full-wave rectifier using four diodes
Full-wave rectifier using a center tap transformer and 2 diodes
full Wave Rectifier with Capacitor Filter
Diode bridgeBridge Rectifierfull wave bridge rectifier circuitfull wave bridge rectifier circuit with capacitor filter - KBPC2504 Bridge Rectifier Diode
- rectifier diode 1n4007





![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}V_{\mathrm {rms} }&={\frac {V_{\mathrm {peak} }}{2}}\\[8pt]V_{\mathrm {dc} }&={\frac {V_{\mathrm {peak} }}{\pi }}\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8d8b3a0bfeadf4d9578fb87c37968464dcf11d53)



![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}V_{\mathrm {dc} }=V_{\mathrm {av} }&={\frac {2V_{\mathrm {peak} }}{\pi }}\\[8pt]V_{\mathrm {rms} }&={\frac {V_{\mathrm {peak} }}{\sqrt {2}}}\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a21f7aabaf22383b8d6641d6364d838f9b95ab61)



No comments:
Post a Comment